[ad_1]
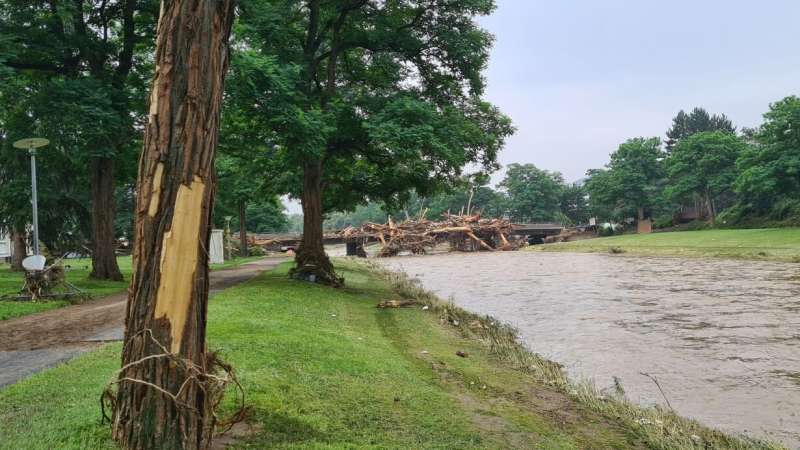

The German governing administration estimates the full losses resulting from the disastrous floods in July 2021 at 32 billion euros. In two scientific tests, 1 of which is at present available in All-natural Dangers and Earth Technique Sciences, scientists at Karlsruhe Institute of Technologies (Package) have investigated how precipitation, evaporation procedures, water stream, and runoff led to this flooding. To increase long term preparedness for such intense functions, they suggest that chance assessments just take greater account of the landscape and river classes, how they transform, and how sediments are transported. In addition, projections display an boost in the spatial extent and frequency of this kind of excessive functions, as properly as greater amounts of precipitation.
The July 2021 flood was one of the 5 worst and costliest purely natural disasters in Europe in the earlier 50 decades. Additional than 180 individuals dropped their life, and perfectly around 10,000 properties had been ruined. Vital infrastructure, e.g. electrical grids, drinking water offer networks, bridges, rail strains and streets, was partly or wholly destroyed. The whole extent of the flooding in the Eifel region on July 14 and 15, 2021, shocked even the authorities. A mix of numerous aspects contributed to this disaster. “We investigated how precipitation, evaporation procedures, drinking water stream, and runoff led to this flooding,” suggests Dr. Susanna Mohr, General Manager of the Heart for Disaster Management and Threat Reduction Engineering (CEDIM) at Kit, who led the interdisciplinary team from various Package institutes that compiled the analyze.
Debris improved both of those extent and influence of Ahr flood
The estimated total of water that flowed by the Ahr River in the 2021 flood was similar to that of the historic floods of 1804 and 1910, but the measured water concentrations were being substantially greater at several spots in 2021. “We noticed that the sort of debris—the material transported by the flowing water—changed significantly. Alongside with eroded sediment and existing deadwood, anthropogenic materials—those designed by people—played a vital part,” states Mohr.
“For illustration, automobiles and trucks, trailers, trash containers and development elements piled up about bridges, which brought on more bottlenecks and exacerbated the results of the flood.” To improve foreseeable future preparedness for this kind of excessive events, Mohr advises that flood possibility administration get the landscape, infrastructure and buildings into account, together with river courses and their changes and opportunity sediment transport, when undertaking hazard assessments.
Total of precipitation not unparalleled
The scientists also when compared the July 2021 precipitation occasion with historic precipitation records. “Our analyses clearly show that the noticed overall precipitation was amongst the highest in Germany in the past 70 yrs, so it was intense but not unprecedented,” says Dr. Florian Ehmele from KIT’s Institute of Meteorology and Local climate Research—Department Troposphere Study (IMK-TRO).
“The precipitation activities that led to the important floods in Berlin and Brandenburg in 1978 or on the Elbe River in 2002 ended up substantially more robust in conditions of both depth and extent or period.” On the other hand, previous precipitation occasions comparable to that of July 2021 were being noticed mainly in eastern and southern Germany and significantly less normally in the west, in accordance to Ehmele.
Simulations display climate transform intensifying long term flood situations
The Kit scientists have also simulated the flood function under numerous climate ailments. “The depth of these precipitation situations will increase by about seven percent with every diploma of warming. The simulations display that the volume of precipitation is already eleven % bigger than below pre-industrial situations,” states Dr. Patrick Ludwig, who heads the regional weather modeling operating team at IMK-TRO. “So we have to assume a further maximize in precipitation as world-wide warming progresses.”
But Ludwig warns that this will not be the only foreseeable future difficulty. “Our projections clearly show that such severe functions will deal with larger locations, last for a longer time and arise a lot more often,” he says.
General public demands superior chance consciousness
The hefty floods of July 2021 confirmed how vital it is to be well prepared for these events and to answer properly, say the researchers. To enhance resilience in the celebration of disasters, which would lower the sum of harm and the range of victims, they urge that in addition to the likely potential risks, social facets and the vulnerability of infrastructure must also be taken into account. An critical element of resilience is public possibility recognition, i.e. information of rapidly and proper doable responses in the occasion of a catastrophe.
Local climate change is building flooding even worse: 3 reasons the planet is observing far more document-breaking deluges
Susanna Mohr et al, A multi-disciplinary investigation of the outstanding flood event of July 2021 in central Europe. Portion 1: Party description and examination, Natural Dangers and Earth Program Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.5194/nhess-2022-137
Quotation:
Local climate change and land-use adjustments raise likelihood of flood events (2022, July 21)
retrieved 5 August 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-07-weather-land-use-chance-gatherings.html
This document is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the reason of private research or investigation, no
portion may perhaps be reproduced with no the published permission. The information is supplied for details reasons only.
[ad_2]
Source link




More Stories
Factors To Consider In Buying A Lawn Mower
Car Buying Tips: Why Does It Make Sense to Buy a Discontinued Car Model?
Sealants For Industrial And Domestic Use – Their Characteristics And Uses